Showing posts with label web2.0. Show all posts
Showing posts with label web2.0. Show all posts
Saturday, May 21, 2011
Changing the World, One Map at a Time
The Ushahidi platform is built on the Kohana web framework, a fork of the CodeIgniter framework. It includes built-in support for Clickatell SMS gateways, and the official Ushahidi-hosted websites use the commercial service. Ushahidi provides the option of using OpenStreetMap maps in its user interface, but requires the Google Maps API for geocoding. Ushahidi is often set up using a local SMS gateway created by a local FrontlineSMS set-up. This video provides a good overview on how the platform is being used around the world.
Source: Wikipedia
Thursday, May 27, 2010
PPgis.net Open Forum on Participatory Geographic Information Systems and Technologies

PPgis.net serves as a global avenue for discussing issues, sharing experiences and good practices related to community mapping, public participation GIS (PPGIS), participatory GIS (PGIS) and other geographic information technologies used to support integrated conservation and development, sustainable natural resource management and customary property rights in developing countries and among indigenous people worldwide.
Members of the network are able to share information and lessons learned, post questions and announcements and upload and download resource documents which are relevant to the practice.
The site is an online gateway for accessing discussion lists in English, French, Spanish and Portuguese, all dealing with participatory mapping.
Thursday, January 21, 2010
The Bulanjao Geotagged Report
On August 2009, a mission led by the Philippines-based Ancestral Land/Domain Watch (ALDAW) and the Centre for Biocultural Diversity (CBCD) at the University of Kent traveled to Barangay Sumbiling, Municipality of Bataraza, Province of Palawan (Philippines).
Geo-referenced audio-visual and photographic documentation was carried out in the Bulanjao range whose vegetation consists of a very unique type of forest growing on ultramafic /heavy-metal rich soils. The area is home to at least four plant species that are classified as vulnerable and two of them have already been included in the IUCN Red List.
 In spite of its unique ecological features, the Bulanjao range has been subjected to mineral exploration and development by the Rio Tuba Nickel Mining Corporation (RTNMC). RTNMC is a Filipino-Japanese partnership holding a mining concession area of about 5,265 hectares.
In spite of its unique ecological features, the Bulanjao range has been subjected to mineral exploration and development by the Rio Tuba Nickel Mining Corporation (RTNMC). RTNMC is a Filipino-Japanese partnership holding a mining concession area of about 5,265 hectares.
RTNMC and its partner, Coral Bay Nickel Corporation (CBNC), need to mine nickel ores as part of the expansion of their new Hydrometallurgical Processing Plant (HPP) project. However, one the conditions specified in the Environmental Compliance Certificate (ECC) issued to them in 2002, is that “core zones” - as identified by the Strategic Environmental Plan for Palawan (Republic Act Republic Act 7611) should not be included in the areas of mining operations and, this, of course includes the Bulanjao range.
 Starting at an elevation of about 40m ASL, the ALDAW/CBCD mission followed the mining road to reach the highest portions of the Bulanjao range. Geo-tagging evidence indicates that erosion on the Bulanjao mining road is occurring also at low elevations. During the rainy season the water creates deep clefts on the roadsides, hence penetrating the soil and fostering road collapse. No mitigating measures have been put into place to reduce erosion. A huge crater-like excavation has been found at 566m ASL. and land slides, induced by road construction, have been documented around the sources of the Sumbiling river, at almost 900m ASL. The latter is the most important water source for both lowland farmers and indigenous communities.
Starting at an elevation of about 40m ASL, the ALDAW/CBCD mission followed the mining road to reach the highest portions of the Bulanjao range. Geo-tagging evidence indicates that erosion on the Bulanjao mining road is occurring also at low elevations. During the rainy season the water creates deep clefts on the roadsides, hence penetrating the soil and fostering road collapse. No mitigating measures have been put into place to reduce erosion. A huge crater-like excavation has been found at 566m ASL. and land slides, induced by road construction, have been documented around the sources of the Sumbiling river, at almost 900m ASL. The latter is the most important water source for both lowland farmers and indigenous communities.
Marylin Samparan, a local IP living in the area told the mission: “time will come when our children will no longer recognize the names of trees, the footprints of animals, the birds’ songs. This will be the time when the forest will be gone, the mining companies will be gone, the rivers will no longer flow…and us? We will still be here”.
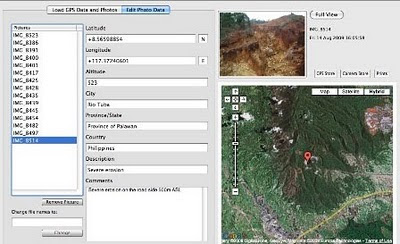
On 15 August 2009, the mission established that mining road had already reached an altitude of 859m ASL – and its exact location was defined through the following GPS coordinates (+ 8.59322548 N Latitude and + 117.36516571 E Longitude).
 Mission’s findings have now been compiled into a geo-tagged report, which is being used by local indigenous communities to support their legal struggle against mining in Bulanjao.
Mission’s findings have now been compiled into a geo-tagged report, which is being used by local indigenous communities to support their legal struggle against mining in Bulanjao.
Source: The ALDAW NETWORK
The ALDAW NETWORK (Ancestral Land/Domain Watch) is an advocacy-campaign network of Indigenous Peoples jointly constituted by NATRIPAL (United Tribes of Palawan) and BANGSA PALAWAN PHILIPPINES (Indigenous Alliance for Equity and Wellbeing) on August 2009.
Geo-referenced audio-visual and photographic documentation was carried out in the Bulanjao range whose vegetation consists of a very unique type of forest growing on ultramafic /heavy-metal rich soils. The area is home to at least four plant species that are classified as vulnerable and two of them have already been included in the IUCN Red List.
 In spite of its unique ecological features, the Bulanjao range has been subjected to mineral exploration and development by the Rio Tuba Nickel Mining Corporation (RTNMC). RTNMC is a Filipino-Japanese partnership holding a mining concession area of about 5,265 hectares.
In spite of its unique ecological features, the Bulanjao range has been subjected to mineral exploration and development by the Rio Tuba Nickel Mining Corporation (RTNMC). RTNMC is a Filipino-Japanese partnership holding a mining concession area of about 5,265 hectares.RTNMC and its partner, Coral Bay Nickel Corporation (CBNC), need to mine nickel ores as part of the expansion of their new Hydrometallurgical Processing Plant (HPP) project. However, one the conditions specified in the Environmental Compliance Certificate (ECC) issued to them in 2002, is that “core zones” - as identified by the Strategic Environmental Plan for Palawan (Republic Act Republic Act 7611) should not be included in the areas of mining operations and, this, of course includes the Bulanjao range.
 Starting at an elevation of about 40m ASL, the ALDAW/CBCD mission followed the mining road to reach the highest portions of the Bulanjao range. Geo-tagging evidence indicates that erosion on the Bulanjao mining road is occurring also at low elevations. During the rainy season the water creates deep clefts on the roadsides, hence penetrating the soil and fostering road collapse. No mitigating measures have been put into place to reduce erosion. A huge crater-like excavation has been found at 566m ASL. and land slides, induced by road construction, have been documented around the sources of the Sumbiling river, at almost 900m ASL. The latter is the most important water source for both lowland farmers and indigenous communities.
Starting at an elevation of about 40m ASL, the ALDAW/CBCD mission followed the mining road to reach the highest portions of the Bulanjao range. Geo-tagging evidence indicates that erosion on the Bulanjao mining road is occurring also at low elevations. During the rainy season the water creates deep clefts on the roadsides, hence penetrating the soil and fostering road collapse. No mitigating measures have been put into place to reduce erosion. A huge crater-like excavation has been found at 566m ASL. and land slides, induced by road construction, have been documented around the sources of the Sumbiling river, at almost 900m ASL. The latter is the most important water source for both lowland farmers and indigenous communities.Marylin Samparan, a local IP living in the area told the mission: “time will come when our children will no longer recognize the names of trees, the footprints of animals, the birds’ songs. This will be the time when the forest will be gone, the mining companies will be gone, the rivers will no longer flow…and us? We will still be here”.
On 15 August 2009, the mission established that mining road had already reached an altitude of 859m ASL – and its exact location was defined through the following GPS coordinates (+ 8.59322548 N Latitude and + 117.36516571 E Longitude).
 Mission’s findings have now been compiled into a geo-tagged report, which is being used by local indigenous communities to support their legal struggle against mining in Bulanjao.
Mission’s findings have now been compiled into a geo-tagged report, which is being used by local indigenous communities to support their legal struggle against mining in Bulanjao.Source: The ALDAW NETWORK
The ALDAW NETWORK (Ancestral Land/Domain Watch) is an advocacy-campaign network of Indigenous Peoples jointly constituted by NATRIPAL (United Tribes of Palawan) and BANGSA PALAWAN PHILIPPINES (Indigenous Alliance for Equity and Wellbeing) on August 2009.
Friday, September 18, 2009
Web-Based GIS and the Future of Participatory GIS Applications within Local and Indigenous Communities
As resource managers search for strategies to meet the challenges posed by intense competition for scarce local resources, the implementation of Community-based GIS applications have become widespread. Besides mapping, the Participatory GIS (PGIS) projects create a peaceful medium for community groups and public officials to meet, exchange views and also learn to develop trust for each other. However, PGIS projects face many problems including the lack of basic supporting infrastructure and services. The adoption of the Internet as a platform for PGIS applications therefore raises concerns about the future of PGIS projects. While the Internet may open the participatory process, it can also hinder participation among local groups. In an era when PGIS applications have become important in the management of local resources, there is an urgent need to examine implications of the On-line PGIS project. Accordingly, in their paper, by the title Web-Based GIS and the Future of Participatory GIS Applications within Local and Indigenous Communities, Peter Kyem and James Saku assess the potential benefits and drawbacks of on-line PGIS applications within local communities.
Saturday, September 20, 2008
Management Change at UNOSAT
According to Alain Retiere, Director of UNOSAT, the programme has reached the required maturity to become independent from the administrative management of UNOPS and become fully part of the new United Nations Institute for Training and Research that the Secretary-General has entrusted ASG Dr. Carlos Lopes to lead together with the United Nations Staff College, in full coordination with the United Nations University. This process will bring to UNOSAT further training activities, which will increasingly be carried out by the United Nations under a unified management. UNOSAT will enjoy the additional opportunity of developing applied research on satellite solutions, and consolidate the UN training offer on satellite applications for key issues ranging from emergency response to sustainable recovery.
In parallel, UNDP has decided to mainstream satellite applications throughout its network of 166 country offices supported by its 40 regional technical centers to help face the main development challenges. A new trend is emerging within the “territorial approach to development”, where a more local and decentralized way of supporting development efforts in most vulnerable countries is being applied. Although all dimensions of the UNDP development agenda will benefit from mainstreamed satellite applications, environment and energy is the area that has been selected as key entry point, considering the urgent need to help local communities to face climate change challenges with the most appropriate tools including satellite and GIS applications.
In parallel, UNDP has decided to mainstream satellite applications throughout its network of 166 country offices supported by its 40 regional technical centers to help face the main development challenges. A new trend is emerging within the “territorial approach to development”, where a more local and decentralized way of supporting development efforts in most vulnerable countries is being applied. Although all dimensions of the UNDP development agenda will benefit from mainstreamed satellite applications, environment and energy is the area that has been selected as key entry point, considering the urgent need to help local communities to face climate change challenges with the most appropriate tools including satellite and GIS applications.
Labels:
geography,
gis,
GIT,
google_earth,
google_maps,
mapping,
media,
neogeography,
participatory,
pgis,
ppgis,
web2.0,
web2fordev
Saturday, September 06, 2008
Information and Communication Technology and Peacebuilding: Summary of a Workshop
Those who would use information and communication technology (ICT) in the cause of peace need to be cognizant of the risks as well as the benefits. ICT can facilitate positive dialogue but also hate speech. It can be used to fight corruption but also facilitate it. Simply giving people more information does not necessarily lead to predictable or positive results. As people become more informed, they may become more motivated to change their circumstances and to do so violently.
On December 14, 2007, the National Academy of Engineering (NAE) convened a group of experts in diverse fields to consider the role of ICT in promoting peace and conflict resolution. The one-day workshop was designed to consider current and emerging technologies and strategies for employing them in conflict management and diplomacy. Giacomo Rambaldi presented a case study on "GIS and Participatory 3-D Modeling in Land-Use Negotiation" . The workshop also aimed to explore how organizations with a role in promoting peace, like the U.S. Institute of Peace, can most effectively leverage technology in carrying out their missions.
"Information and Communication Technology and Peacebuilding: Summary of a Workshop" reviews the group's discussions on number of key issues, illuminates certain practitioner needs, and suggests possible next steps.
The proceedings can be downloaded for free via this link.
On December 14, 2007, the National Academy of Engineering (NAE) convened a group of experts in diverse fields to consider the role of ICT in promoting peace and conflict resolution. The one-day workshop was designed to consider current and emerging technologies and strategies for employing them in conflict management and diplomacy. Giacomo Rambaldi presented a case study on "GIS and Participatory 3-D Modeling in Land-Use Negotiation" . The workshop also aimed to explore how organizations with a role in promoting peace, like the U.S. Institute of Peace, can most effectively leverage technology in carrying out their missions.
"Information and Communication Technology and Peacebuilding: Summary of a Workshop" reviews the group's discussions on number of key issues, illuminates certain practitioner needs, and suggests possible next steps.
The proceedings can be downloaded for free via this link.
Tuesday, August 26, 2008
African Indigenous Peoples’ Workshop on effective use of ICTs in environmental advocacy
Starting on August 26, 2008 IPACC is holding a 3 day workshop outside of Windhoek Namibia for 40 indigenous African leaders to review case studies of how geo-spatial information technologies can be used by indigenous peoples to express their traditional ecological knowledge to decisions makers for the purposes of securing recognition and rights. The workshop will also look at the role of the internet (Web 2.0) in helping promote good advocacy and communication. The event is co-hosted and presented by the Technical Centre for Agricultural and Rural Cooperation (CTA), the Rainforest Foundation UK, ERMIS Africa, Cybertracker Conservation and Shalin Ry.
Labels:
ethics,
geo,
geography,
GIT,
p3dm,
participation,
participatory,
web2.0
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)
